Data and Governance | Data Interpretation | UGC NET Paper 1
Get Study Materials of General Studies for UPPSC ⇒ DOWNLOAD NOW
Data Governance (DG) is the exercise of decision making and an authority for data related matters.
Data Governance refers to the organizational bodies, rules, decision rights, and accountabilities of people and information systems as they perform information-related processes.
Data and Governance
UNIT VII
– Data Interpretation (Click on the topic to
read)
|
It is an umbrella term for an emerging discipline that consists a number of different practices for, data management, data quality, business process management, and risk management. The goal of Data Governance is to ensure that the data serves the organisational purposes in a sustainable way.
Wikipedia explains as “Data Governance encompasses the people, processes, and information technology required to create a consistent and proper handling of an organisation’s data across the business enterprise. Goals may be defined at all levels of the enterprise and doing so may aid in acceptance of processes by those who will use them.”
We can conclude as “Data Governance includes the people, processes and technologies needed to manage and protect the company’s data assets in order to guarantee generally understandable, correct, complete, trustworthy, secure and discoverable corporate data.”
The data governance may include the followings:
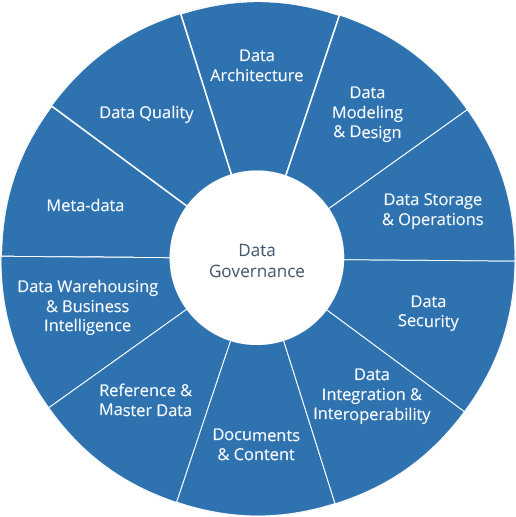
DG is about establishing methods, and an organization with clear responsibilities and processes to standardise, integrate, protect and store organisational data. The main goals of data governance are to:
- Establish internal rules for data use
- Implement compliance requirements
- Minimize risks
- Reduce costs
- Increase the value of data
- Facilitate the administration of the above
- Help to ensure to be existence of the company through risk management and optimization
- Improve internal and external communication
Need for Data and Governance
Effective data governance creates a framework for the use of data that fits each organisation. Data governance improves operational efficiency, application effectiveness, and minimizes risk.
Because of data governance, not only do the right people get the right information at the right time, but they also get it in the right way both for their immediate purposes and in a way that works with the data framework for the whole organisation.
Why Enterprises Struggle with Data and Governance
The followings are the most common barriers to success for Data Governance initiatives:
Organisational: Different groups within an organization must communicate and coordinate well with one another
Data quality, Data Management, and data migration integration: Applications and data must speak to one another, and this must be addressed upfront and planned for in any integration initiative
Accountability and ownership of data: People must be held accountable for information assets and supported with technology to ensure the integrity of the assets
Cost: DG initiatives must be implemented in such a way that costs are recouped, and business value is proven
Effective Data Governance
The following are the steps using a repeatable technological framework to ensure effective Data Governance:
- Prioritise areas for business improvement
- Maximize availability of information assets
- Create roles, responsibilities, and rules
- Improve and ensure information asset integrity
- Establish an accountability infrastructure
- Convert to a master data-based culture
- Develop a feedback mechanism for process improvement
Useful links
Social links
Useful links
Contact Us
Address: B 14-15, Udhyog Marg, Block B, Sector 1, Noida, Uttar Pradesh 201301
Alpha-I Commercial Belt, Block E, Alpha I, Greater Noida, Uttar Pradesh 201310
